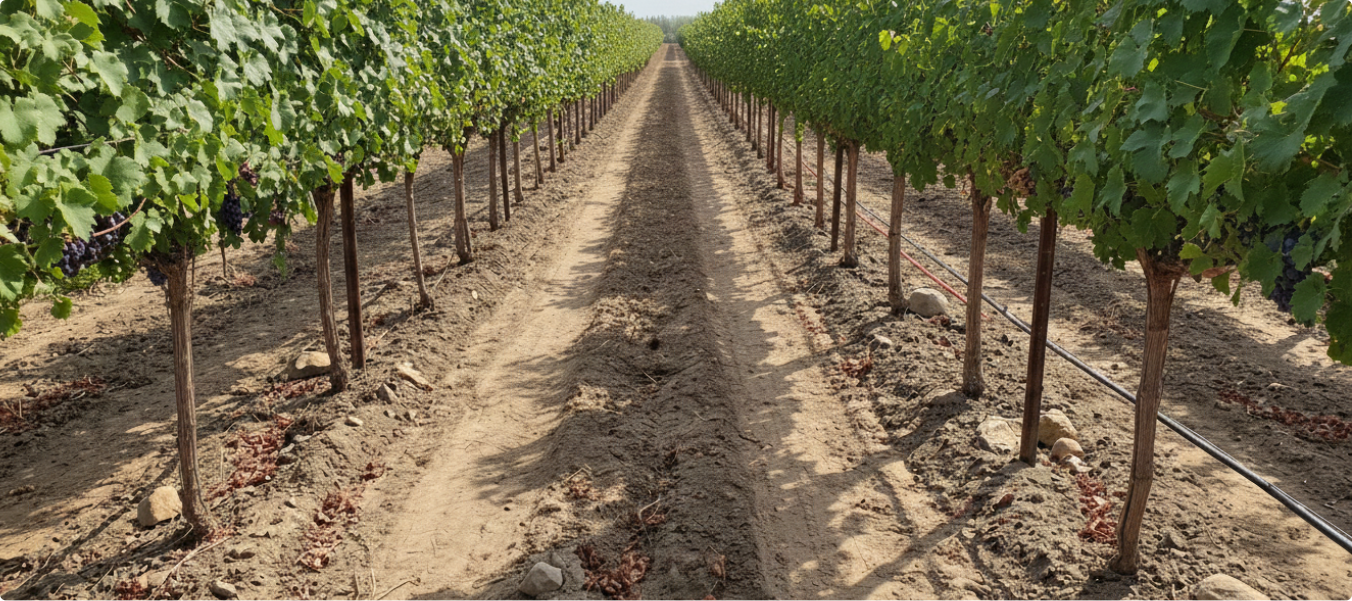
Agriculture
AGRICULTURE
Industry Challenges in Agriculture AI
- High variability in crop and soil conditions
- Need for automated crop inspection and disease identification
- High‑volume image datasets needs precise annotations for ML training
- Demand for insights to improve sustainability and productivity
How rProcess Supports the Agriculture Ecosystem
We deliver high‑precision datasets that fuel next‑generation agricultural AI, empowering smarter crop monitoring, autonomous field operations, geospatial insights, and precision farming innovations.
Annotation Services for Agriculture
- Semantic & instance segmentation
- Crop disease & pest and weed detection
- Plant species classification
- Growth stage analysis
- Navigation cues for autonomous machinery
- 3D object detection
- Multi-sensor (LiDAR–Camera–RADAR) alignment
- Drivable area detection
- Terrain classification
- Spatial understanding for autonomous farming robots
- RADAR labeling for low-visibility perception
- Satellite & aerial segmentation
- Land-use & field boundary mapping
- Multi-spectral soil and vegetation profiling
Why Choose rProcess?
Precision Annotation for Complex Natural Environments
Our teams specialize in accurately labeling diverse agricultural conditions, ensuring your AI models perform reliably across real‑world field environments.
Scalable Workforce and Quick Ramp‑Up
We rapidly deploy trained teams to manage large, multi‑sensor agricultural datasets, delivering high-volume outputs without delays.
Customized QA Workflow Ensuring 97%+ Accuracy
Our multi‑step QA process is tailored for agricultural data, consistently achieving 97%+ accuracy for production-grade AI training.
Certified and Compliant Operations
Your data is protected under globally recognized standards, TISAX, ISO 9001:2015, ISO 27001:2022, RBA Platinum, and GDPR compliance, ensuring secure and responsible handling.
Agriculture Case Studies
AI models for agricultural automation require accurate datasets that can distinguish between various farm regions and objects. Manual classification of landscapes such as tilled fields, un-tilled fields, and tree buffers is time-consuming and inconsistent, limiting the scalability of automation systems.
- Annotated farm images using segmentation techniques to classify key regions and objects:
- Tilled fields
- Un-tilled fields
- Roads
- Buffers
- Trees
Established structured annotation workflows with ~30 minutes per task for consistent labeling.
- Delivered a dataset of 20,000 annotated images with high-quality segmentation.
- Enabled AI models to automatically detect and classify farm landscapes.
- Enhanced the accuracy of agricultural automation systems for land-use monitoring and farm planning.


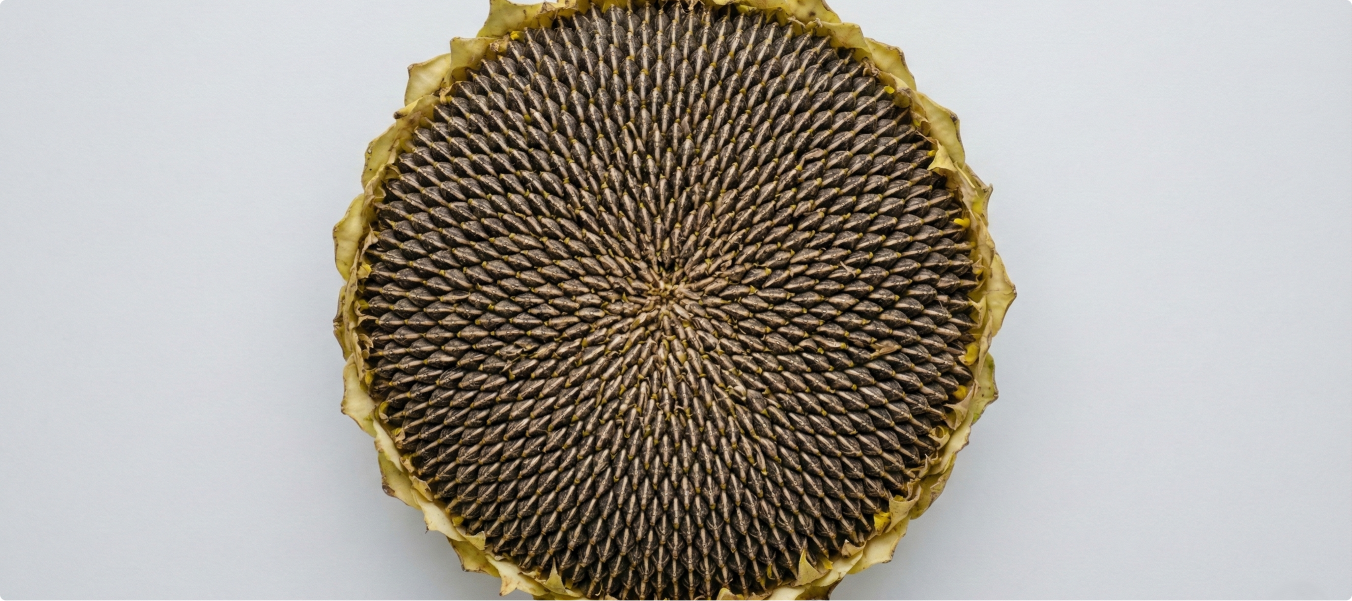
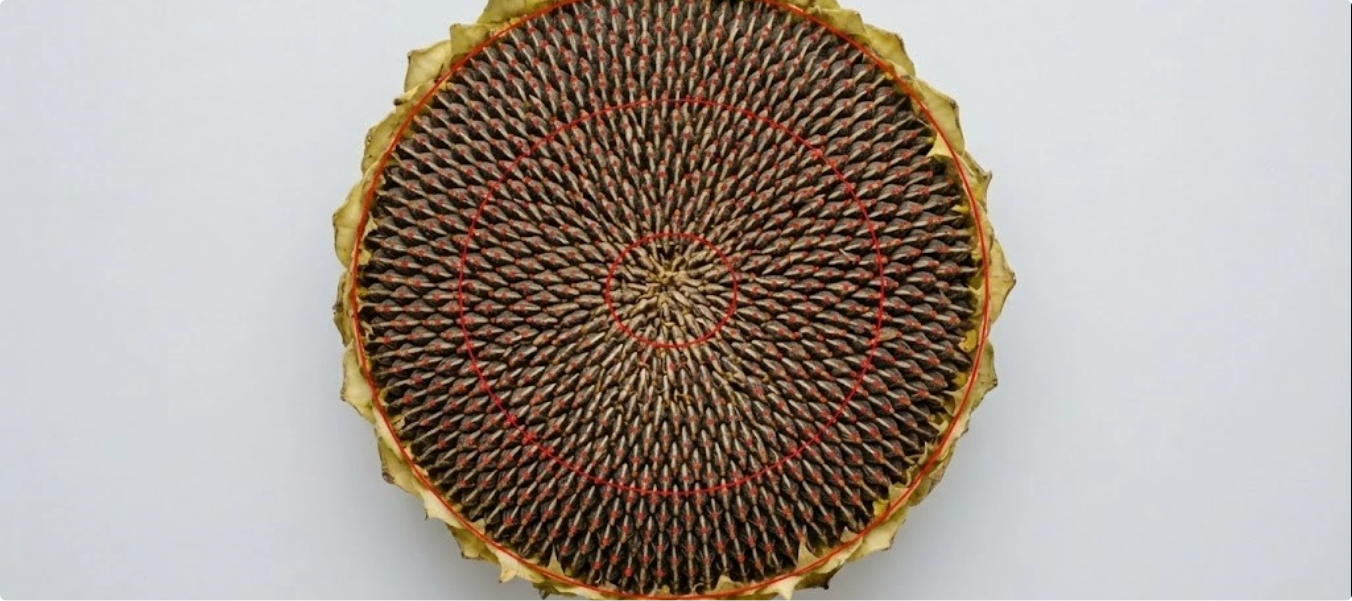
Studying seed patterns and growth in sunflowers is critical for crop research, yield prediction, and breeding. Traditional manual analysis is slow and lacks the precision needed to train AI models for large-scale agricultural insights.
- Annotated sunflower heads using ellipse and keypoint labeling techniques.
- Marked key regions and seed points to capture growth and distribution patterns.
- Applied efficient workflows: 10 mins per keypoint annotation and 5 mins per ellipse annotation.
- Successfully annotated 50,000 images.
- Created a high-quality dataset enabling AI models for yield prediction and breeding research.
- Delivered accurate insights into seed arrangement, density, and growth trends to support agricultural innovation.


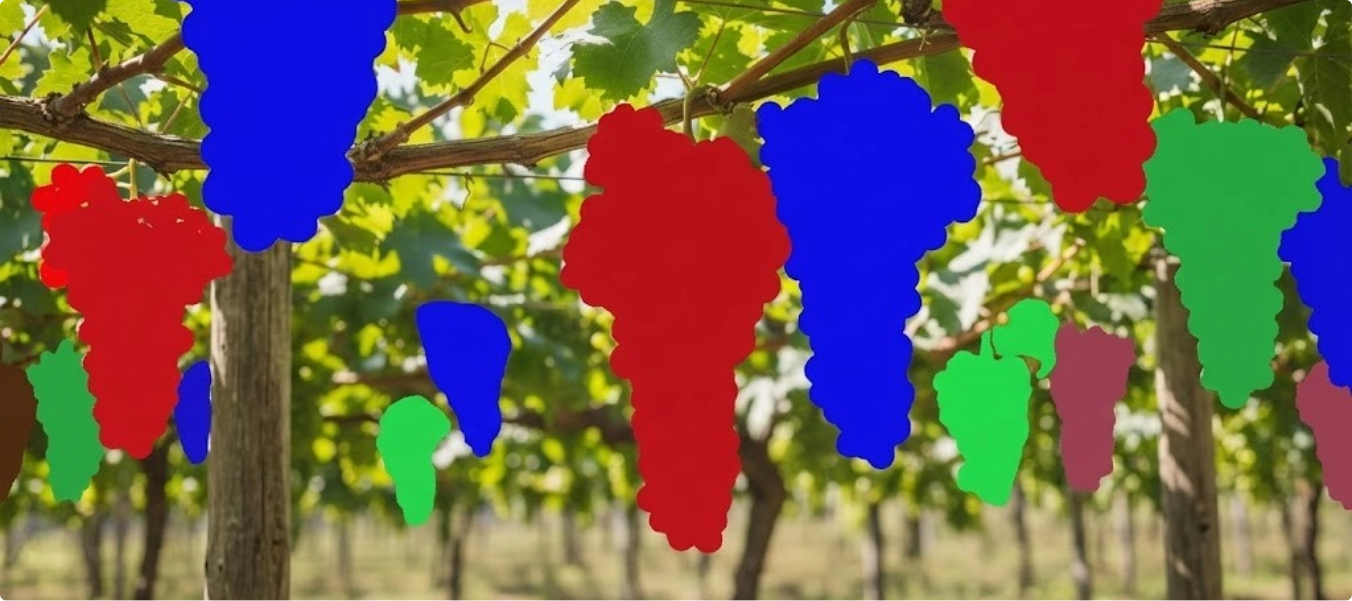
Automated harvesting and crop monitoring systems require precise data to detect, locate, and evaluate fruits and vegetables. Traditional manual methods are labor-intensive and cannot scale effectively for real-time analytics.
- Annotated fruits and vegetables using segmentation techniques for accurate shape and location mapping.
- Focused on multiple produce types with tailored annotation times: Grapes – 35 mins per task & Apples/Oranges – 10 mins per task
- Created datasets optimized for robotic harvesting and plant analytics.
- Successfully annotated 10,000 images across diverse fruits and vegetables.
- Delivered datasets that enable automated picking systems and real-time crop monitoring.
- Improved machine accuracy in identifying and evaluating produce for agricultural automation.


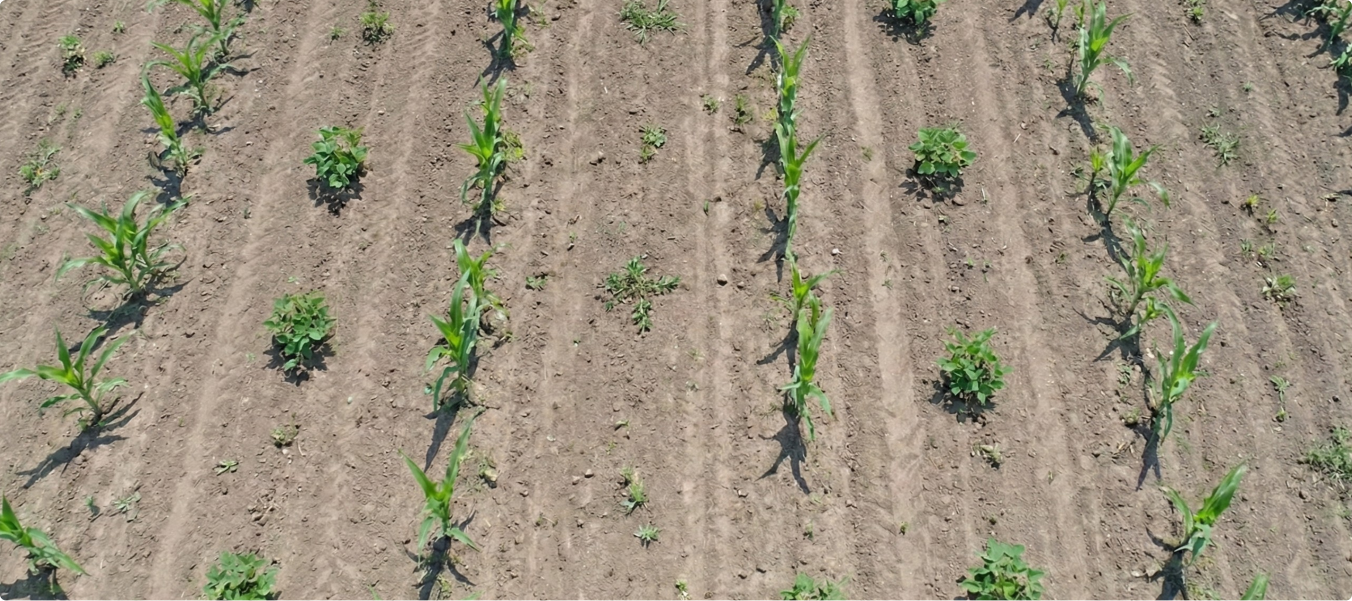
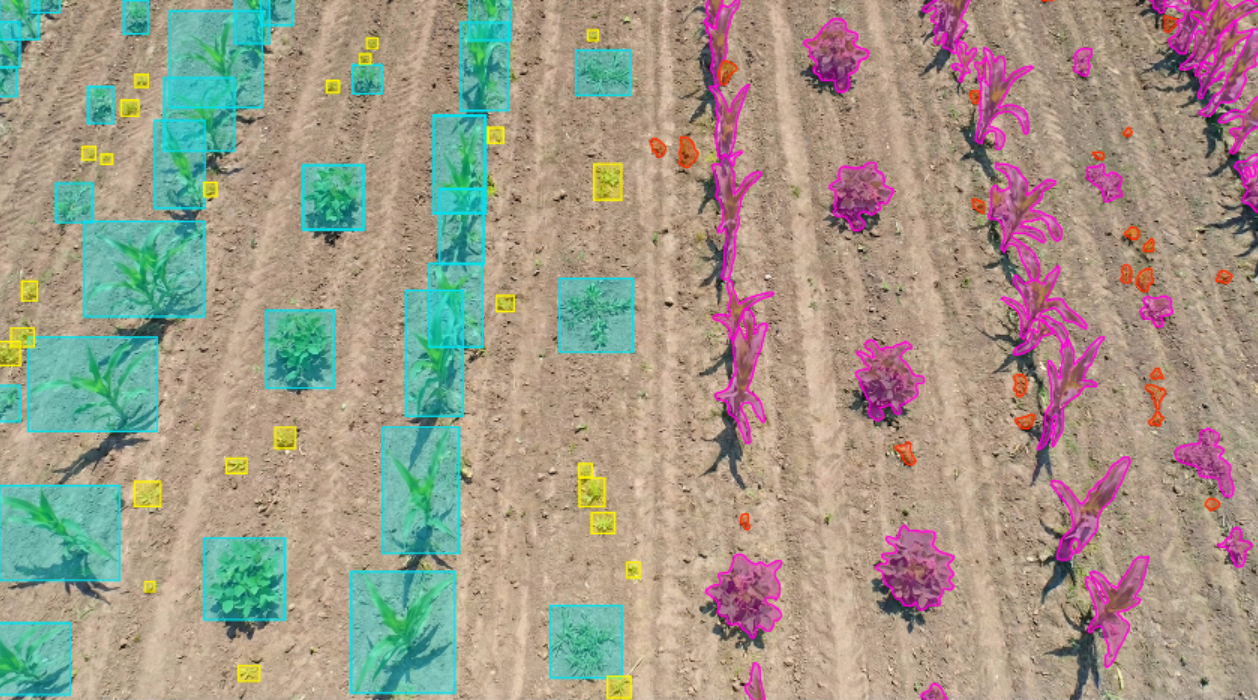
Efficient farming requires distinguishing crops from weeds to optimize chemical usage. Traditional blanket spraying methods waste resources, increase costs, and damage the environment. There was a need for high-quality labeled datasets to train AI-powered See & Spray technology that targets weeds precisely.
- Labeled farm images to differentiate Soybean and Corn crops from weeds.
- Applied segmentation (15 mins per image) and bounding box annotation (3 mins per image) to ensure accurate classification.
- Created structured datasets enabling machine learning models to guide smart sprayers.
- Successfully annotated 500,000 images.
- Delivered high-accuracy segmentation and bounding box datasets.
- Enabled AI-driven spraying systems to reduce chemical use, cut costs, and support sustainable farming


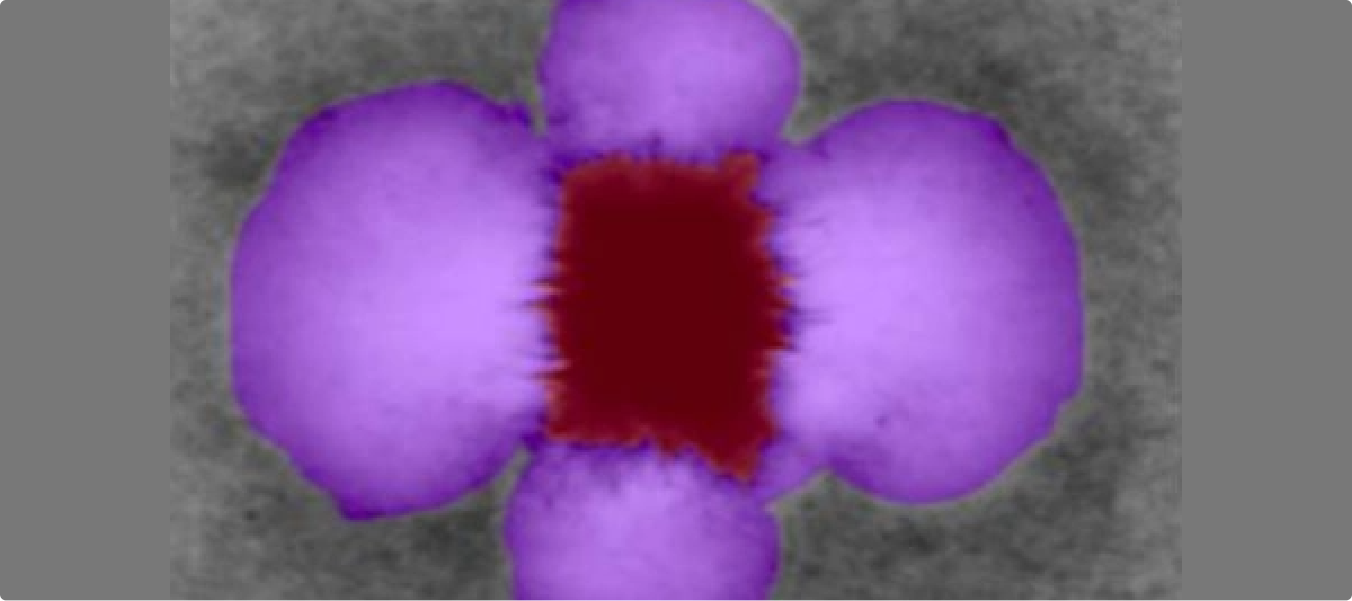
Accurately identifying and segmenting aster structures and fluid flumes in microscopy images is essential for agricultural research and plant biology studies. The challenge lies in achieving precise segmentation from raw, non-annotated images to ensure reliable datasets for analysis.
- Deployed a 2D annotation workflow designed for agricultural microscopy.
- Applied segmentation techniques to isolate aster and fluid flume regions.
- Ensured high-quality, research-ready datasets through systematic annotation.
- Segmented 500 raw microscopy images with precision.
- Achieved accurate segmentation using 2D annotation tools tailored for agricultural imaging.
- Maintained efficiency with an average 5 minutes per task, ensuring timely project delivery.
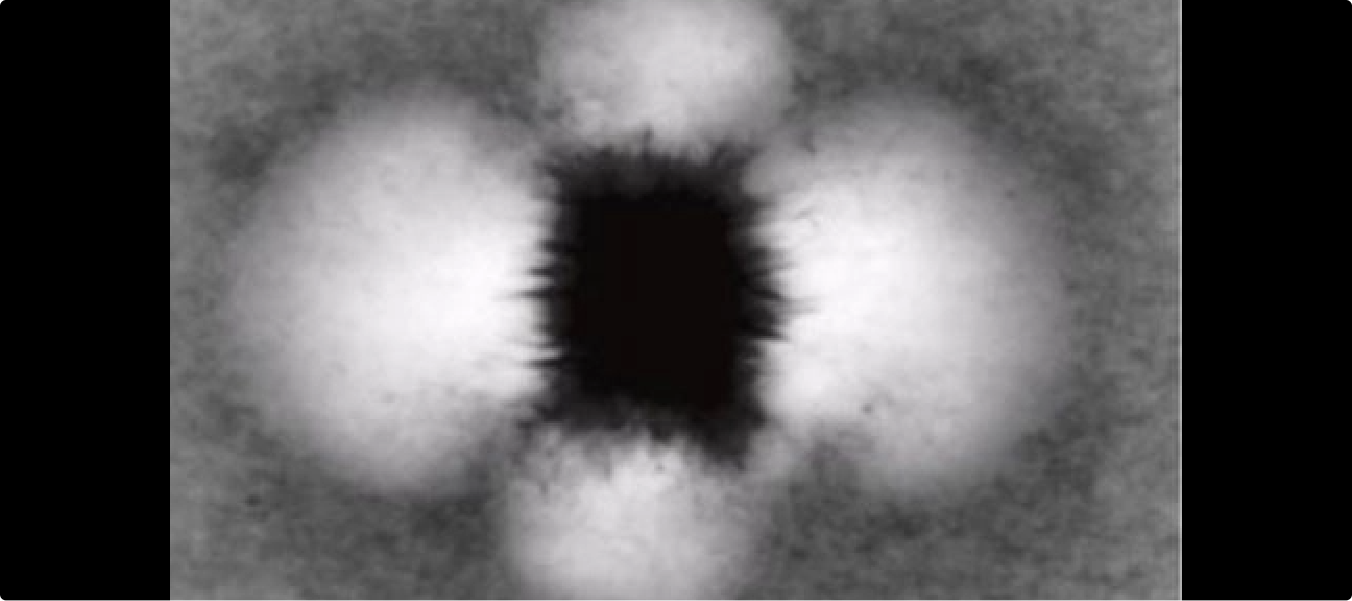

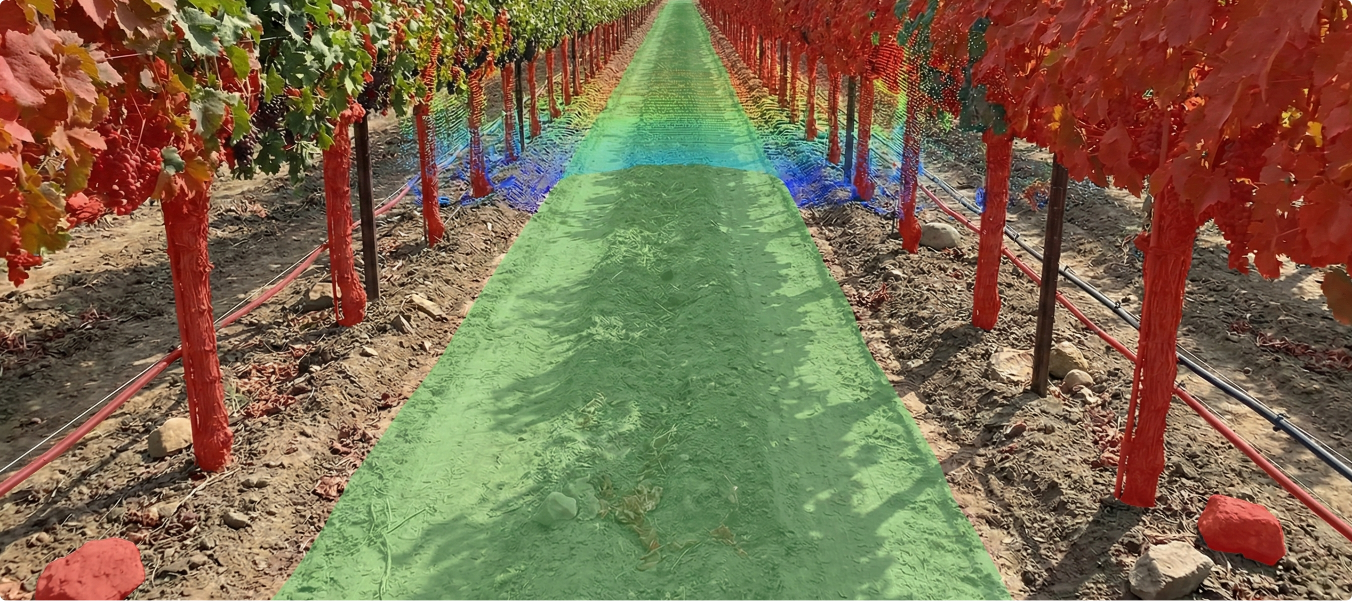
Agricultural machines need to detect and navigate row entry points accurately to operate efficiently in large-scale farmlands. Manual identification of row gateways from LiDAR-derived images is labor-intensive and inconsistent, making it difficult to scale automation.
- Annotated Bird’s Eye View height map images derived from LiDAR.
- Labeled row entry points (“gateways”) using polyline annotation techniques.
- Established an efficient annotation process with ~1 minute per task for fast turnaround.
- Delivered a dataset of 30,000 high-quality annotated images.
- Enabled AI models to automatically detect and navigate row entrances in agricultural fields.
- Improved automation for agricultural machinery, reducing reliance on manual navigation.


